21-03-15 자바스크립트로 하는 자료구조와 알고리즘(10)
18장 고급 문자열
- 트라이(trie)는 문자열을 검색해 저장된 문자열 중 일치하는 문자열이 있는지 확인하는데 주로 사용되는 특별한 종류의 트리
- 트라이는 중첩 객체를 사용해 구현되는데 각 노드는 자신과 직접 연결된 자식들을 지니고 이 자식들은 키 역할을 한다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63class TrieNode {
constructor() {
this.children = {};
this.endOfWord = false;
}
}
class Trie {
constructor() {
this.root = new TrieNode(); // 생성되면 하나의 트라이 노드를 갖는다
}
insert(word) {
let current = this.root; // 현재 노드값을 가져옴 이 노드에는 children 객체와 endOfWord가 존재함
for (let i = 0, len = word.length; i < len; i++){
let ch = word.charAt(i);
let node = current.children[ch]; // 객체(children{})내 항목 참조
if (node === null) {
node = new TrieNode();
current.children[ch] = node;
}
current = node;
}
current.endOfWord = true;
}
search(word) {
let current = this.root;
for (let i = 0, len = word.length; i < len; i++) {
let ch = word.charAt(i);
let node = current.children[ch];
if (node === null) {
return false;
}
current = node;
}
return current.endOfWord;
}
delete(word) {
this.deleteRecursively(this.root, word, 0);
}
deleteRecursively(current, word, index) {
if (index === word.length) {
if (!current.endOfWord) return false
current.endOfWord = false;
return Object.keys(current.children).length === 0;
}
let ch = word.charAt(index),
node = current.children[ch];
if (node === null) return false;
let shouldDeleteCurrentNode = this.deleteRecursively(node, word, index+1);
// shouldDeleteCurrentNode의 리턴은 boolean값이므로 이 값이 true라면 삭제해야 한다
if(shouldDeleteCurrentNode) {
delete current.children[ch];
return Object.keys(current.children).length === 0;
}
return false
}
} - 보이어-무어 문자열 검색
- 텍스트 편집기 어플리케이션과 웹 브라우저의 ‘찾기’기능에 사용됨
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11const buildBadMatchTable = str => {
let tableObj = {},
strLength = str.length;
for (let i = 0; i < strLength - 1; i++) {
tableObj[str[i]] = strLength - 1 - i;
}
if (tableObj[str[strLength-1]] === undefined) {
tableObj[str[strLength-1]] = strLength;
}
return tableObj;
} - 보이어-무어 문자열 검색 알고리즘의 구현
- 패턴으로 사용할 문자열을 입력받을 때 검색하고자 하는 현재 문자열이 불일치 표에 존재하면 인덱스를 건너 뛴다
- 현재 문자열이 불일치 표에 존재하지 않다면 인덱스를 1 증가시킴
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23const boyerMoore = (str, pattern) => {
let badMatchTable = buildBadMatchTable(pattern),
offset = 0,
patternLastIndex = pattern.length - 1,
scanIndex = patternLastIndex,
maxOffset = str.length - pattern.length;
while (offset <= maxOffset) {
scanIndex = 0;
while (pattern[scanIndex] === str[scanIndex + offset]) {
if (scanIndex === patternLastIndex) {
return offset;
}
scanIndex++;
}
let badMatchString = str[offset + patternLastIndex];
if (badMatchTable[badMatchString]) {
offset += badMatchTable[badMatchString]
} else {
offset += 1;
}
}
return -1;
} - 보이어-무어 알고리즘은 최선의 경우 모든 문자가 동일할 때이고 이 때의 시간 복잡도는 O(W/T)이다 (이때, W는 패턴을 찾고자 하는 대상인 문자열)
- 최악의 경우 패턴이 문자열의 끝에 존재하고 앞부분이 모두 고유의 문자로 구성된 경우고 이 때의 시간 복잡도는 O(T*W)가 된다
- 이보다 조금 더 빠른 구현을 위해서는 커누스-모리스-플랫 문자열 검색 알고리즘(이후 KMP 알고리즘)을 사용할 수 있다
- KMP 알고리즘은 입력 텍스트 T 내에서 단어 W의 출현 횟수를 검색한다
- 접두사 배열을 만들 때 접두사 배열이 동일한 접두사를 얻기 위해 인덱스를 얼마나 되돌려야 할지를 나타낼 수 있도록 해야 한다
- 접두사 표 만들고 KMP 검색
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38const longestPrefix = str => {
let prefix = new Array(str.length);
let maxPrefix = 0;
prefix[0] = 0;
for (let i = 1, len = str.length; i < len; i++) {
while (str.charAt(i) !== str.charAt(maxPrefix) && maxPrefix > 0) {
maxPrefix = prefix[maxPrefix - 1];
}
if (str.charAt(maxPrefix) === str.charAt(i)) {
maxPrefix++;
}
prefix[i] = maxPrefix;
}
return prefix;
}
const KMP = (str, pattern) => {
let prefixTable = longestPrefix(pattern),
patternIndex = 0,
strIndex = 0;
while (strIndex < str.length) {
if (str.charAt(strIndex) !== pattern.charAt(patternIndex)) {
if (patternIndex !== 0) {
patternIndex = prefixTable[patternIndex - 1];
} else {
strIndex++;
}
} else if (str.charAt(strIndex) === pattern.charAt(patternIndex)) {
strIndex++;
patternIndex++;
}
if (patternIndex === pattern.length) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
} // 시간 복잡도는 O(W) - 라빈-카프 검색 알고리즘은 텍스트에서 특정 패턴을 찾기 위해 해싱을 활용한다
- 해시 함수(라빈 지문 해싱 기법)를 통해 부분 문자열이 패턴과 동일한지 비교하는 과정의 속도를 높인다
- 라빈 지문
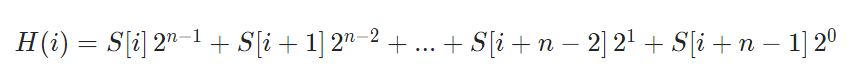
- 라빈 지문을 이용한 해시 함수
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53class RabinKarpSearch {
constructor () {
this.prime = 101;
}
rabinkarpFingerprintHash (str, endLength) {
if (endLength === null) endLength = str.length;
let hashInt = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < endLength; i++) {
hashInt += str.charCodeAt(i) * Math.pow(this.prime, i);
}
return hashInt;
}
recalculate (str, oldIndex, newIndex, oldHash, patternLength) {
if (patternLength === null) patternLength = str.length;
let newHash = oldHash - str.charCodeAt(oldIndex);
newHash = Math.floor(newHash/this.prime);
newHash += str.charCodeAt(newIndex) * Math.pow(this.prime, patternLength - 1);
return newHash;
}
strEquals (str1, startIndex1, endIndex1, str2, startIndex2, endIndex2) {
if(endIndex1 - startIndex1 !== endIndex2 - startIndex2) return false;
while (startIndex1 <= endIndex1 && startIndex2 <= endIndex2) {
if (str1[startIndex] !== start2[startIndex2]) {
return false;
}
startIndex1++;
startIndex2++;
}
return true;
}
rabinkarpSearch (str, pattern) {
let T = str.length,
W = pattern.length,
patternHash = this.rabinkarpFingerprintHash(pattern, W),
textHash = this.rabinkarpFingerprintHash(str, W);
for (let i = 1; i <= T - W + 1; i++) {
// strEquals (str1, startIndex1, endIndex1, str2, startIndex2, endIndex2)
if (patternHash === textHash && this.strEquals(str, i - 1, i + W - 2, pattern, 0, W - 1)) {
return i - 1;
}
if (i < T - W + 1) {
// recalculate (str, oldIndex, newIndex, oldHash, patternLength)
textHash = this.recalculateHash(str, i - 1, i + W - 1, textHash, null);
}
}
return -1;
}
} - 라빈-카프 알고리즘은 원본 자료가 있는 경우 표절 검사 등에 사용될 수 있다