5장 연습문제 다시 보기
1 | const findSumBetter = (arr, weight) => { |
1 | const findSumBetter = (arr, weight) => { |
1 | let cache = {}; |
1 | const knapsackDP = (idx, weights, values, target, matrix) => { |
1 | if (두 수열의 마지막 글자가 일치한다면) { |
1 | const LCSNaive = (str1, str2, str1Length, str2Length) => { |
1 | const longestCommonSequenceLength = (str1, str2) => { |
coinChange(S, M, n) = coinChange(S, M-1, N) + coinChanges(S, M, N-Sm)1 | // coinArr의 인덱스는 [0, ..., coinIndex] |
1 | const countCoinWaysDP = (coinArr, coinIndex, total) => { |
1 | if (문자가 동일하다) |
1 | const editDistanceRecursive = (str1, str2, length1, length2) => { |
1 | const editDistanceDP = (str1, str2, length1 = str1.length, length2 = str2.length2) => { |
a = 1100, b = 1010일 때, a & b = 1000이다a = 1100, b = 1010일 때, a & b = 1110이다a = 1100, b = 1010일 때, a & b = 0110이다a = 1100일 때 NOT a = 0011이다 9(1001) << 1 = 10010(2) = 18, 9 << 2 = 100100(2) = 36 9(1001) >> 1 = 100(2) = 41 | // 이진수를 더하기는 두 수를 더한 다음 10을 초과하면 1을 다음 수로 올린다 (carry) |
1 | class TrieNode { |
1 | const buildBadMatchTable = str => { |
1 | const boyerMoore = (str, pattern) => { |
1 | const longestPrefix = str => { |
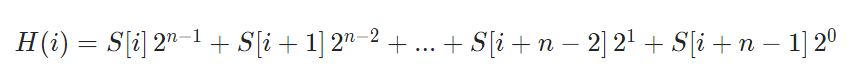
1 | class RabinKarpSearch { |
1 | class Heap { |
1 | class MinHeap extends Heap{ |
1 | bubbleDown() { |
| 노드 | 인덱스 |
|---|---|
| 자신 | N |
| 부모 | (N - 1) / 2 |
| 왼쪽 자식 | (N * 2) + 1 |
| 오른쪽 자식 | (N * 2) + 2 |
1 | /* |
1 | let arr = [12, 3, 13, 4 ,2, 40, 23]; |
| 단어 | 뜻 |
|---|---|
| 정점 | 그래프를 형성하는 노드로 원으로 표기 |
| 간선 | 그래프에서 노드 간의 연결로 정점(원)사이의 선으로 표기 |
| 정점 차수 | 해당 점점에 연결된 간선의 개수 |
| 희소 그래프 | 정점들 간 가능한 연결 중 일부만 존재하는 경우 |
| 밀집 그래프 | 다양한 정점들 간에 연결이 많은 경우 |
| 순환 그래프 | 어떤 정점에서 출발해 해당 정점으로 다시 돌아오는 경로가 있는 지향성 그래프 |
| 가중치 | 간선에 대한 값으로 문맥에 따라 다양한 것을 나타냄(정점 간 거리 등) |
1 | class UndirectedGraph { |
1 | class DirectedGraph { |
1 | function _isEmpty(obj) { |
1 | // class DirectedGraph 내부라고 가정 |
1 | class BinaryTreeNode { |
1 | // 선순위 |
1 | class BinarySearchTree { |
1 | class AVLTree { |
1 | function findLowestCommonAncester(root, value1, value2) { |
1 | const printKthLevels = (root, k) => { |
1 | const isSameTree = (root1, root2) => { |
1 | /* |
1 | class SinglyLinkedListNode { |
1 | // 위에서 이어짐 |
1 | remove(value) { |
1 | deleteHead() { |
1 | find (value) { |
1 | class DoubleLinkedListNode { |
1 | insertHead (value) { |
1 | deleteHead () { |
1 | deleteTail() { |
1 | findFromHead (value) { |
1 | const reverseSinglyLinkedList = sll => { |
1 | const deleteDuplicateDataInSLL = sll => { |
1 | const deleteDuplicateDataInSLL = sll => { |
1 | class LFUNode { |
1 | class DLLNode { |
1 | class HashTable { |
1 | class HashTable { |
1 | put(key, value) { |
1 | put(key, value) { |
1 | class Stack { |
1 | const stackAccessNthTopNode = (stack, n) => { |
1 | const stackSearch = (stack, element) => { |
1 | class Queue { |
1 | const queueAccessNthTopNode = (queue, n) => { |
1 | class TwoStackQueue { |
1 | class QueueStack { |
1 | class Customer { |
1 | const BracketVerification = string => { |
1 | class sortableStack { |
let exampleSet = new Set();1 | const intersectSets = (setA, setB) => { |
1 | const isSuperSet = (setA, subSet) => { |
1 | const unionSet = (setA, setB) => { |
1 | const unionSetWithSpreadOperator = (setA, setB) => { |
1 | const differenceSet = (setA, setB) => { |
1 | const checkDupl = arr => { |
1 | const uniqueList = (arr1, arr2) => { |
1 | const linearSearch = (arr, n) => { |
1 | const binarySearch = (arr, n) => { |
1 | const swap = (arr, idx1, idx2) => { |
1 | const selectionSort = items => { |
1 | const insertionSort = items => { |
1 | const quickSort = arr => { |
1 | // 정렬되지 않은 목록에서 k번째로 작은 항목을 찾기 |
1 | const merge = (leftArr, rightArr) => { |
1 | const countSort = arr => { |
arr.sort((a,b) => a-b)와 같이 사용한다1 | const sqrtIntNaive = num => { |
1 | const sqrtInt = num => { |
1 | const findTwoSum = (arr, sum) => { |
1 | const findOnlyOnce = (arr, low, high) => { |
1 | const sortByStringLength = arr => { |
1 | const wordCnt = sentence => { |
1 | const classExample = () => { |
1 | let obj = {}; |
1 | let one = document.getElementById('one'); |
1 | let test = { prop : 'test' } |
1 | const colorCount = arr => { |
1 | // for문을 활용한 함수 |
1 | const getFibo = n => { |
1 | const getFiboBetter = (n, lastlast, last) => { |
1 | const pascalTriangle = (row, col) => { |
1 | const pascalTriangle = (row, col) => { |
1 | // 1. base condition |
1 | // 1. base condition : beginIndex === endIndex; |
1 | const dictionary = { |
1 | const isPalindrome = word => { |
array[1]과 같이 특정 인덱스에 접근한다면 메모리 주소로부터 직접 값을 얻어온다 (Java처럼 메모리 주소값을 알 수 있는 방법은 거의 없다, 스택오버플로우 참고)while(true)와 같이 for( ; ;)로도 무한루프를 구현할 수 있다for (index in arr) 이나 for (element of arr)와 같이 사용할 수 있다 1 | // 얕은 복사 |
1 | const findSum = (arr, weight) => { |
1 | const findSumBetter = (arr, weight) => { |
1 | const medianOfArray = arr => { |
1 | const commonElements = kArray => { |
1 | let M = [ |
1 | const checkRow = (rowArr, letter) => { |
1 | const findChar = (char, matrix) => { |
1 | const rotateMatrix = matrix => { |
author.bio
author.job