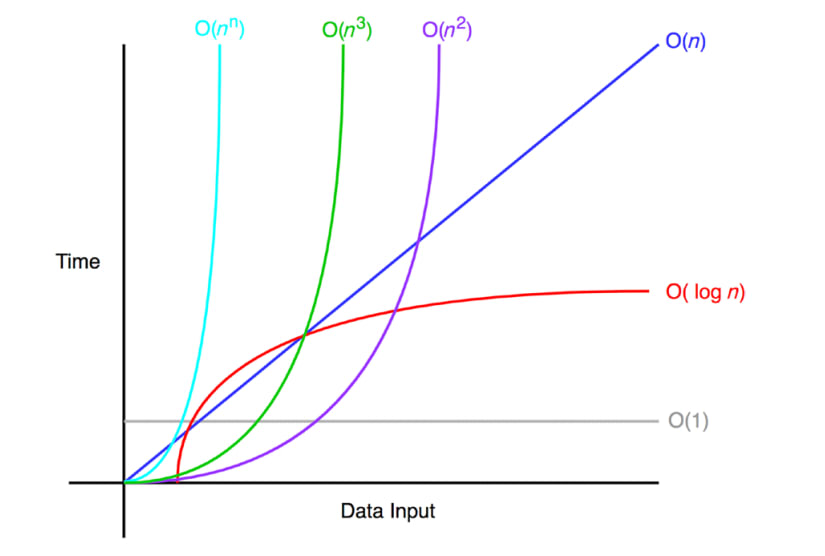
13장 연결 리스트
- 연결 리스트란 각 노드가 달느 노드를 가리키는 자료구조이다
- 고정된 크기를 갖는 배열과는 달리 실행 시간에 메모리를 할당하거나 해제할 수 있는 동적 자료구조
- 연결 리스트 자료구조는 각 노드가 다음 노드에 대한 참조를 갖는 자료구조로 data와 next속성이 있다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17class SinglyLinkedListNode {
constructor (data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null; // 노드 마지막 연결지점은 null값임
}
}
class SinglyLinkedList {
constructor () {
this.head = null;
this.size = 0;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size === 0;
}
} - 연결 리스트의 시작을 헤드라고 부르고 이 값은 아무 항목도 삽입되지 않으면 null이다
- 연결 리스트의 헤드가 비어있는 경우엔 신규 노드로 설정되고 비어있지 않다면 예전 헤드가 temp에 저장된 후에 새로운 헤드가 신규로 추가된 노드가 된다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10// 위에서 이어짐
insert(value) {
if (this.head === null) this.head = new SinglyLinkedListNode(value);
else {
let temp = this.head;
this.head = new SinglyLinkedListNode(value);
this.head.next = temp;
}
this. size++;
} - 단일 연결 리스트에서 노드를 삭제하는 것은 해당 노드의 참조를 제거함으로써 구현할 수 있다
- next가 가리키는 노드를 찾고 해당 노드의 next 주소값을 이전 노드의 next값으로 할당하면 노드를 삭제할 수 있다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31remove(value) {
let currHead = this.head;
if (currHead.data === value) {
// 삭제하고자 하는 노드가 지금 데이터와 같다면 헤드를 다음 노드로 변경하고 사이즈를 줄임
this.head = currHead.next;
this.size--;
} else {
// 헤드를 prv로 저장하고
let prev = currHead;
while (currHead.next) {
// next 주소값이 null이 아닐때까지 순회한다
if (currHead.data === value) {
// 해당 값을 찾았다면 이전 값의 next를 현재 값의 next로 변경 (중간 잘라냄)
prev.next = currHead.next;
// prev값을 지금 head로 변경
prev = currHead;
currHead = currHead.next;
break;
}
prev = currHead;
currHead = currHead.next;
}
if (currHead.data === value) {
// 삭제하는 노드의 next 주소값은 null로 변경하여 잘라내기
prev.next = null;
}
this.size--;
}
} - 연결 리스트의 헤드에 있는 항목을 삭제하는 것은 O(1)만에 가능한데 맨 처음에 있는 값이기 때문
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10deleteHead() {
let toReturn = null;
if (this.head !== null) {
toReturn = this.head.data;
this.head = this.head.next;
this.size--;
}
return toReturn;
} - 연결 리스트 내의 값을 검색하려면 모든 next 포인터를 반복순회해야한다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10find (value) {
let currHead = this.head;
while(currHead.next) {
if (currHead.data === value) {
return true;
}
currHead = currHead.next;
}
return false;
} - 이중 연결 리스트는 양방향 단일 연결 리스트 같은 것이다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19class DoubleLinkedListNode {
constructor (data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class DoubleLinkedList {
constructor () {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
isEmpty () {
return this.size === 0;
}
} - 양방향으로 연결되어 있으므로 노드들은 next와 prev 둘 다 갖는다
- 헤드에 항목을 삽입하는 것은 prev 포인터를 갱신해야 한다는 점 빼고는 단일 연결 리스트와 같다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18insertHead (value) {
if (this.head === null) {
// 헤드가 비어있다면 이 헤드에 새로운 값을 갖는 노드를 추가
this.head = new DoublyLinkedListNode(value);
this.tail = this.head;
// 단 하나만 있을 경우에 이 노드가 헤드이자 테일이기 때문
} else {
// 이미 헤드가 있다면 임시로 노드를 만들고
let temp = new DoublyLinkedListNode(value);
// 만든 노드의 next값을 현재 헤드값으로 변경하고
temp.next = this.head;
// 현재 헤드값의 prev값을 새로 만든 노드로 설정한다 (양방향이므로)
this.head.prev = temp;
// 새로 만든 노드가 새 헤드가 된다 (있었던 헤드가 밀려남)
this.head = temp;
}
this.size++;
} - 헤드를 삭제할 때 연결 리스트가 하나의 노드라면 prev와 next 모두 null로 설정해야 하며 여러개 존재하는 경우 삭제하는 헤드의 next값을 헤드로 설정한다
- 신규 헤드의 prev값을 null로 설정하여 참조를 제거한다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16deleteHead () {
let toReturn = null;
if (this.head !== null) {
toReturn = this.head.data;
if (this.tail === this.head) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else {
this.head = this.head.next;
this.head.prev = null;
}
}
this.size--;
return toReturn; // dequeue와 같은 방식임
} - 테일 항목 삭제도 헤드 삭제와 같은 방식으로 제거한다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17deleteTail() {
let toReturn = null;
if(this.tail !== null) {
toReturn = this.tail.data;
if (this.tail === this.head) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else {
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
}
}
this.size--;
return toReturn;
} - 양항향 연결 리스트에서는 헤드에서 헤드의 next 포인터를 사용할 수 있다 (반대로도 가능)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8findFromHead (value) {
let currHead = this.head;
while (currHead.next) {
if (currHead.data === value) return true;
currHead = currHead.next;
}
return false;
} - 단일 연결 리스트 뒤집기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13const reverseSinglyLinkedList = sll => {
let node = sll.head;
let prev = null;
// 방향성을 반대로 바꾸는 과정
while (node) {
let temp = node.next;
node.next = prev;
prev = node;
if (!temp) break;
node = temp;
}
return node;
} - 연결 리스트에서 중복된 항목 제거하기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17const deleteDuplicateDataInSLL = sll => {
let track = [];
let temp = sll.head;
let prev = null;
while (temp) {
if (track.indexOf(temp.data) >= 0) {
prev.next = temp.next;
sll.size--;
} else {
track.push(temp.data);
prev = temp;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
console.log(temp);
} - 개선하기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16const deleteDuplicateDataInSLL = sll => {
let track = {};
let temp = sll.head;
let prev = null;
while (temp) {
if(track[temp.data]) {
prev.next = temp.next;
sll.size--;
} else {
track[temp.data] = true;
prev = temp;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
console.log(temp);
}14장 캐싱
- 캐싱은 자료를 임시 메모리에 저장하는 과정으로 대표적인 캐싱 방법에는 LFU(Least Frequently Used) 캐싱과 LRU(Least Recently Used) 캐싱이 있다
- 최근에 접근한 메모리 위치를 다시 접근할 가능성이 높고(시간적 지역성), 최근에 접근한 메모리 위치 주변의 위치를 다시 접근할 가능성이 높다(공간적 지역성)
- LFU 캐싱은 운영체제가 메모리를 관리하기 위해 사용하는 캐싱 알고리즘으로 가장 참조 빈도가 낮은 항목을 삭제한다
- LFU 캐시는 이중 연결 리스트를 사용해 O(1)시간에 항목을 제거한다
- LFU의 노드에는 freqCount 속성이 있다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123class LFUNode {
constructor (key, value) {
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
this.key = key;
this.data = data;
this.freqCount = 1;
}
}
class LFUDoublyLinkedList {
constructor () {
this.head = new LFUNODE('buffer head', null);
this.tail = new LFUNODE('buffer tail', null);
this.head.next = this.tail;
this.tail.prev = this.head;
this.size = 0;
}
insertHead (node) {
node.next = this.head.next;
this.head.next.prev = node;
this.head.next = node;
node.prev = this.head;
this.size++;
}
removeTail () {
let oldTail = this.tail.prev;
let prev = this.tail.prev;
prev.prev.next = this.tail; // 전 전 노드의 next를 테일로 지정
this.tail.prev = prev.prev; // 테일을 제거하면 테일 앞 값을 테일로 지정해주어야 함
this.size--;
return oldTail;
}
removeNode(node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
this.size--;
}
/*
LFU의 set을 구현하기 위해서는 신규 항목의 삽입과 예전 항목의 교체가 필요함
신규 항목을 삽입할 때 신규 노드가 생성되고 캐시 capacity가 꽉차지 않았다면 freq의 빈도 이중 연결 리스트에 삽입할 수 있다
캐시가 꽉 찬 경우 빈도 이중 연결 리스트의 테일 항목이 삭제된 다음 삽입된다
*/
set(key, value) {
let node = this.keys[key];
if (node === undefined) {
node = new LFUNode(key, value);
this.keys[key] = node;
if (this.size !== this.capacity) {
if (this.freq[1] === undefined) {
this.freq[1] = new LFUDoublyLinkedList();
}
this.freq[1].insertHead(node);
this.size++
} else {
let oldTail = this.freq[this.minFreq].removeTail();
delete this.keys[oldTail.key];
if (this.freq[1] === undefined) {
this.req[1] = new LFUDoublyLinkedList();
}
this.freq[1].insertHead(node);
this.minFreq = 1;
} else {
let oldFreqCount = node.freqCount;
node.data = value;
node.freqCount++;
this.freq[oldFreqCount].removeNode(node);
if (this.freq[node.freqCount] === undefined) {
this.freq[node.freqCount] = new LFUDoublyLinkedList();
}
this.freq[node.freqCount].insertHead(node);
if (oldFreqCount === this.minFreq
&& Object.keys(this.freq[oldFreqCount]).size === 0) {
this.minFreq++;
}
}
}
}
get (key) {
let node = this.keys[key];
if (node === undefined) return null;
else {
let oldFreqCount = node.freqCount;
node.freqCount++;
this.freq[oldFreqCount].removeNode(node);
if (this.freq[node.freqCount] === undefined) {
this.freq[node.freqCount] = new LFUDoublyLinkedList();
}
this.freq[node.freqCount].insertHead(node);
if (oldFreqCount === this.minFreq
&& Object.keys(this.freq[oldFreqCount]).length === 0) {
this.minFreq++;
}
return node.data;
}
}
}
class LFUCache {
constructor (capacity) {
this.key = {}; // LFUNode를 저장하는 공간
this.freq = {};// LFUDoublyLinkedList를 저장하는 공간
this.capacity = capacity;
this.minFreq = 0;
this.size = 0;
}
} - LRU 캐싱은 가장 오래된 항목을 먼저 제거하는 캐싱 알고리즘이다
- 캐시의 항목에 접근하면 해당 항목은 리스트의 뒤(가장 최신)로 이동하고 가장 앞에 있는 항목이 제거되며 새 항목은 가장 뒤에 추가된다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61class DLLNode {
constructor (key, data) {
this.key = key;
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class LRUCache {
constructor (capacity) {
this.keys = {};
this.capacity = capacity;
this.head = new DLLNode('', null);
this.tail = new DLLNode('', null);
this.head.next = this.tail
this.tail.prev = this.head;
}
removeNode (node) {
let prev = node.prev,
next = node.next;
prev.next = next;
next.prev = prev;
}
addNode (node) {
let realTail = this.tail.prev;
realTail.next = node;
this.tail.prev = node;
node.prev = realTail;
node.next = this.tail;
}
get (key) {
let node = this.keys[key];
if (node === undefined) return null;
else {
this.removeNode(node);
this.addNode(node);
return node.data;
}
}
set (key, value) {
let node = this.keys[key];
if (node) this.removeNode(node);
let newNode = new DLLNode(key, value);
this.addNode(newNode);
this.keys[key] = newNode;
if (Object.keys(this.keys).length > this.capacity) {
let realHead = this.head.next;
this.removeNode(realHead);
delete this.keys[realHead.key];
}
}
} - 대부분의 경우 LFU는 LRU보다 성능이 떨어진다 LFU는 특정 시점에 한해 자주 사용된 경우를 배제할 수 없기 때문